Network Processing Units (NPUs) have become a cornerstone of high-performance networking. As data centers scale, 5G traffic grows, and security workloads increase, networking platforms must deliver ultra-low-latency packet processing and advanced flow intelligence—far beyond what general-purpose CPUs can handle efficiently.
This guide explains what NPUs are, how they work, and where they are used, with a clear and enterprise-grade perspective suitable for systems architects, network engineers, and equipment manufacturers.
📘 What Is an NPU (Network Processing Unit)?

An NPU (Network Processing Unit) is a specialized processor designed to accelerate packet processing, routing, traffic management, and security functions in high-speed networks.
Unlike CPUs, which optimize for sequential computing, NPUs use parallel pipelines and hardware accelerators optimized for tasks such as:
Packet parsing & classification
Routing lookups (L2/L3 forwarding)
Tunnel encapsulation (VXLAN, MPLS)
QoS enforcement & traffic shaping
Encryption/decryption for secure transport
Deep packet inspection (DPI)
Stateful firewalling
NPUs are central to modern switches, routers, security gateways, carrier-grade edge nodes, and 5G base station infrastructure.
📘 Why NPUs Matter in Modern Networking
High-Performance Packet Processing
NPUs are built to handle millions of packets per second with deterministic latency.
Typical strengths include:
Deterministic, wire-speed performance
Multi-threaded packet engines
Hardware-accelerated flow tables
Real-time flow security
Lower Latency vs CPUs & GPUs
Processor | Strength | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility & general compute | Higher latency for packet workloads | |
Massive parallel compute | Optimized for matrix math, not packet I/O | |
NPU | Packet-centric acceleration & line-rate forwarding | Not a general compute core |
📘 NPU Architecture Overview
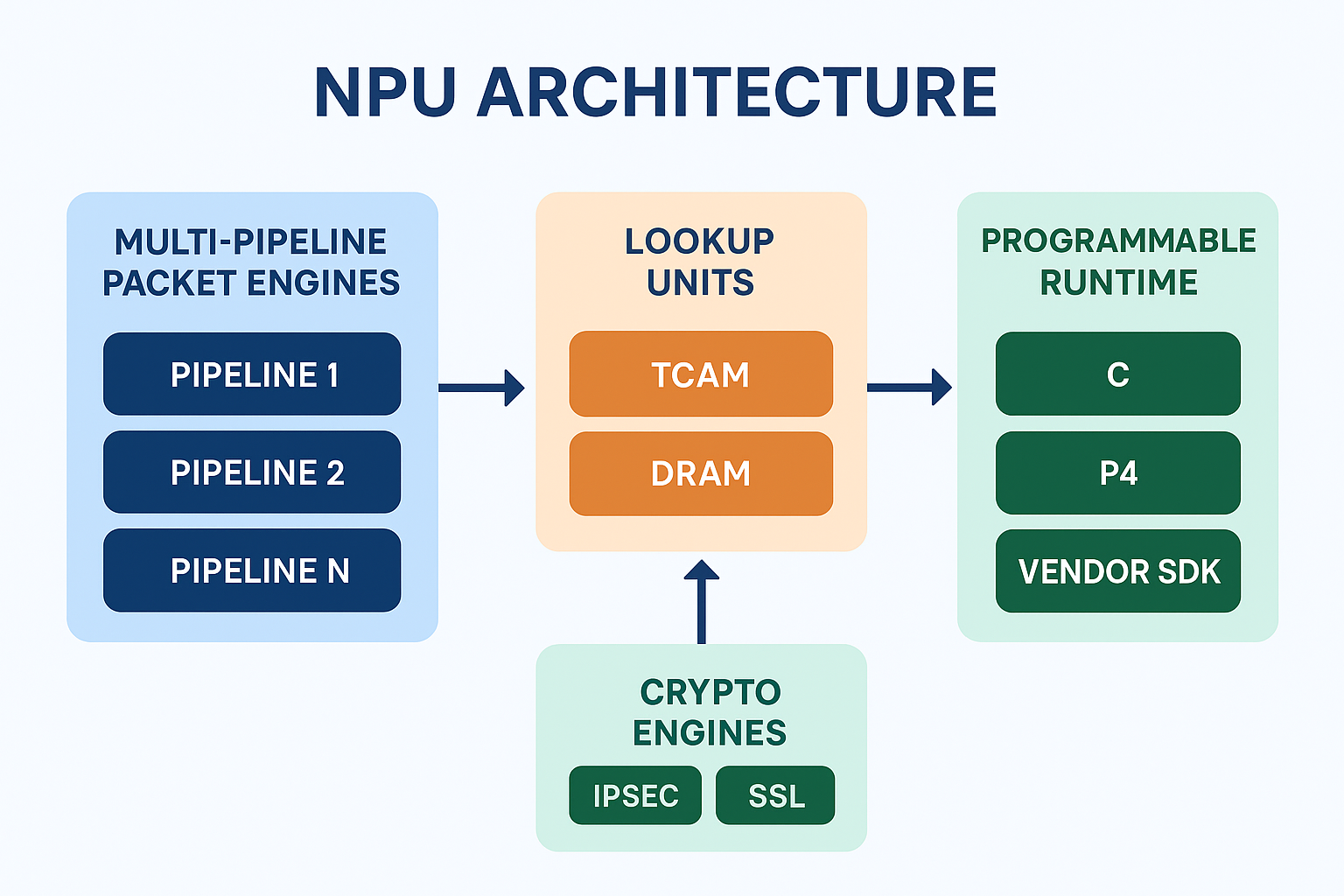
Key Architectural Components
Multi-pipeline packet engines for parallel packet flows
TCAM/DRAM lookup units for routing tables & ACLs
Crypto engines for IPsec/SSL offload
Traffic scheduling & QoS logic
Programmable runtime (C / P4 / vendor SDK)
Programmable NPUs vs Fixed-Function NPUs
Type | Description | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
Fixed-function NPU | ASIC-like, optimized pipelines | High-throughput routers |
Programmable NPU | Flexible via C/P4 programming | SDN & network-virtualization nodes |
📘 Core Applications of NPUs
1. Carrier-Grade Routing & Switching
Core and aggregation routers
5G RAN and transport
Broadband access platforms
2. Data Center Fabric & Cloud Edge
Leaf/spine switches
VXLAN and EVPN data plane
Hardware-accelerated SDN
3. Security & Inspection Systems
IPS/IDS
DDoS mitigation systems
4. Enterprise & Industrial Networking
Industrial Ethernet & gateway devices
📘 NPUs vs Network Switch ASICs vs SmartNICs
Technology | Key Role | Relative Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
Switch ASIC | Pure forwarding, ultra-high throughput | Low |
NPU | Programmable packet processing | Medium-High |
SmartNIC (DPUs) | Virtualized network offload for servers | High |
Many vendors combine NPUs and switch ASICs for hybrid flexibility + throughput.
📘 Leading NPU Platforms
Broadcom Jericho & Qumran families
Marvell OCTEON®
Intel/Barefoot Tofino (P4-programmable)
Huawei Solar NPU
Cisco QuantumFlow Processor
📘 NPU Trends Shaping the Future
Programmable Data Planes
P4 language adoption in data center networking
Customizable packet metadata pipelines
AI-Assisted Networking
Traffic anomaly detection
Adaptive routing
Intelligent QoS policies
Convergence: NPUs + DPUs
For edge computing and cloud offload platforms.
📘 NPU Use Cases in LINK-PP Ecosystem

LINK-PP provides Ethernet magnetics, RJ45 connector modules, and networking interconnect solutions that support NPU-based routers, firewalls, switches, and IoT gateways.
Typical product categories supporting NPU systems include:
PoE RJ45 connectors for intelligent edge devices
High-speed Ethernet magnetic modules
Optical transceivers (1G/10G/25G)
Industrial-temperature network interfaces
Explore magnetic RJ45 and high-speed connectivity solutions for NPU-powered platforms: https://www.l-p.com
📘 Conclusion
Network Processing Units are foundational to next-generation networks—delivering line-rate packet processing, security, and programmability without sacrificing latency or scalability.
With NPUs powering 5G, cloud infrastructure, SD-WAN, and secure industrial networks, understanding their architecture and performance role is essential for modern network design.
FAQs
Q1: Are NPUs the same as GPUs?
No. GPUs excel at matrix math and AI compute; NPUs specialize in packet-level processing.
Q2: Do NPUs replace CPUs in network hardware?
No. NPUs handle packet forwarding, while CPUs manage control-plane and orchestration tasks.
Q3: Can NPUs be programmed?
Yes—modern NPUs support C, P4, or vendor SDK programming models.


