
▶ RTU Overview
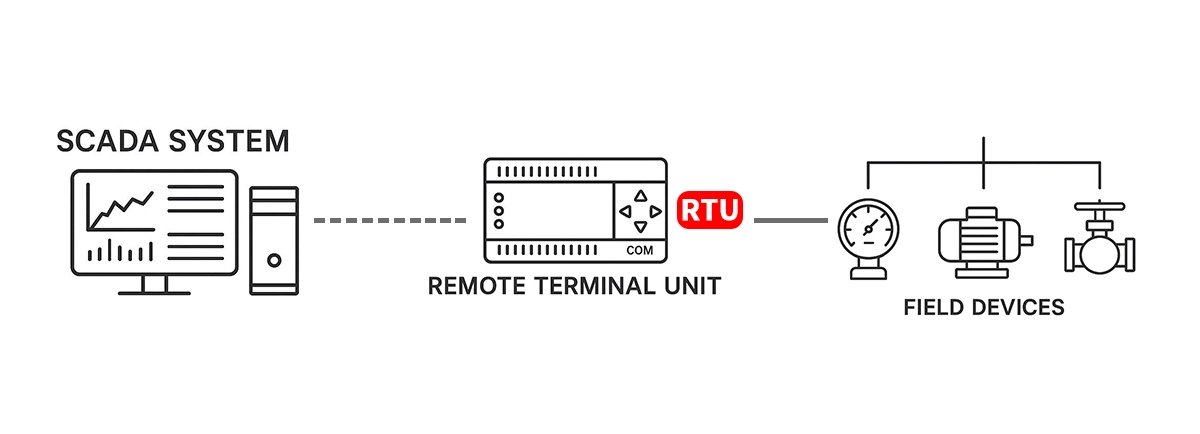
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) are field-deployed, microprocessor-based devices designed to interface between field equipment and supervisory control systems. They collect measurement data, execute control logic, and transmit real-time status, alarms, and events to SCADA or DCS systems. RTUs are engineered for remote, rugged, and often unmanned environments, making them essential in electric utilities, oil & gas pipelines, water systems, transportation, and industrial energy networks.
▶ What an RTU Does

Core capabilities
Data acquisition: Analog and digital signal measurement from sensors, transmitters, meters
Local logic: Event triggers, basic control sequences, time-stamped alarms
Command execution: Operating relays, switches, pumps, and valves
Telecontrol communication: Sending telemetry to SCADA and receiving control commands
Event recording: Logging abnormal conditions and fault records
Cybersecurity features: Authentication, access control, encrypted sessions (in modern designs)
Typical interfaces
Digital Inputs (DI) — breaker status, alarms
Analog Inputs (AI) — 4–20 mA, 0–10 V, voltage/frequency signals
Digital Outputs (DO) — relays, contact closure
Analog Outputs (AO) — proportional control signals
Communication Ports — RS-232, RS-485, fiber, cellular, radio, industrial Ethernet
▶ RTU vs PLC
Item | RTU | PLC |
|---|---|---|
Primary role | Remote monitoring & telecontrol | Fast local automation & motion control |
Strength | Robust communications & remote reliability | Millisecond-level logic execution |
Deployment | Substations, pipelines, remote water sites | Manufacturing lines, machinery |
Power profile | Often low-power / solar-ready | Typically higher power |
Rule of thumb:
RTU = communications & telemetry in harsh/remote sites
PLC = fast industrial control in plant environments
In modern systems, RTUs and PLCs are often integrated, not competing.
▶ Communication Protocols Used by RTUs
Modbus (RTU / TCP)
A widely-adopted and simple request-response protocol for telemetry.
Modbus RTU — serial
Modbus TCP — Ethernet
DNP3
Designed for electric power automation and critical infrastructure; supports time-stamping, unsolicited events, and robust reporting.
IEC 60870-5 / IEC 60870-5-104
Common in European and global utility telecontrol applications; supports remote station-to-master communication in power systems.
IEC 61850 (in modern RTUs)
Used in substation automation with advanced messaging, including GOOSE and MMS services.
▶ Environmental & Reliability Considerations
RTUs must endure:
Wide temperature variation
Lightning/surge exposure
Unstable power or solar supply
Dust, humidity, vibration
Field devices often run for 10-20+ years without frequent site visits. Hardware ruggedness is not optional—it is mission-critical.
▶ RTU Cybersecurity Best Practices
Unique, role-based access credentials
Enforced encryption and secure protocols where supported
Network segmentation between OT and IT networks
Disable unused ports/services
VPN or encrypted tunnel for remote maintenance
Time sync for reliable logs (NTP / PTP)
Firmware update policy & trusted signing
▶ Hardware Connectivity: Why Ethernet Matters
Modern RTUs increasingly rely on Ethernet-based SCADA architectures and industrial IP networks. Reliable physical-layer design is key to availability.
Key Ethernet Interface Requirements
Integrated magnetics for signal integrity
PoE options for powering field devices
EMI/ESD protection
Industrial temperature rating
Mechanical durability for field cabinets
▶ LINK-PP Solutions for RTUs and Industrial Gateways

RTU and edge gateway manufacturers depend on rugged, high-performance connectors to maintain reliable data links.
Recommended LINK-PP features for RTU communication ports:
Integrated RJ45 MagJack with isolation transformers
10/100/1000Base-T support
Industrial temperature options
EMI shielding & surge protection
PoE / PoE+ capable variants for field devices
LINK-PP provides compatible RJ45 magnetics and Ethernet connector solutions used in industrial automation, power grid equipment, and remote telemetry platforms.
▶ Deployment Checklist
Define I/O count, scan rate, and protocol needs
Validate SCADA master/RTU protocol compatibility
Harden device credentials & disable unused services
Use industrial-grade Ethernet magnetics/ports
Implement surge and grounding design
Plan remote firmware & logging strategy
▶ Conclusion
Remote Terminal Units remain foundational to modern industrial control and SCADA systems. As utilities and critical infrastructure modernize toward Ethernet-based and cybersecurity-hardened architectures, RTUs must combine proven field durability with modern protocols and secure communication interfaces.
High-performance physical network components—such as LINK-PP industrial Ethernet connectors and MagJacks—help ensure reliable communication in demanding field environments, reduce maintenance cycles, and safeguard mission-critical telemetry operations.


