
✅ What Is a Backplane?
A backplane is a large printed circuit board that provides high-speed electrical interconnection and power distribution between multiple plug-in cards inside a chassis. Unlike a motherboard, a backplane typically contains passive components such as high-density connectors and controlled-impedance PCB traces.
Backplanes are widely used in switches, routers, telecom equipment, blade servers, storage enclosures, and industrial control systems.
To support these platforms, LINK-PP provides high-performance Integrated RJ45 Connectors, which can be integrated into backplane-based systems.
✅ Why Backplanes Are Critical in High-Speed Systems
Modern systems rely on backplanes to deliver high-bandwidth, low-latency communication across internal modules.
Typical applications include:
Line card ↔ switch fabric connectivity
Blade server midplane interconnect
Hot-swap I/O module connections
40G/100G Ethernet in-chassis transmission
Backplane channels allow systems to scale while maintaining reliability and signal integrity.
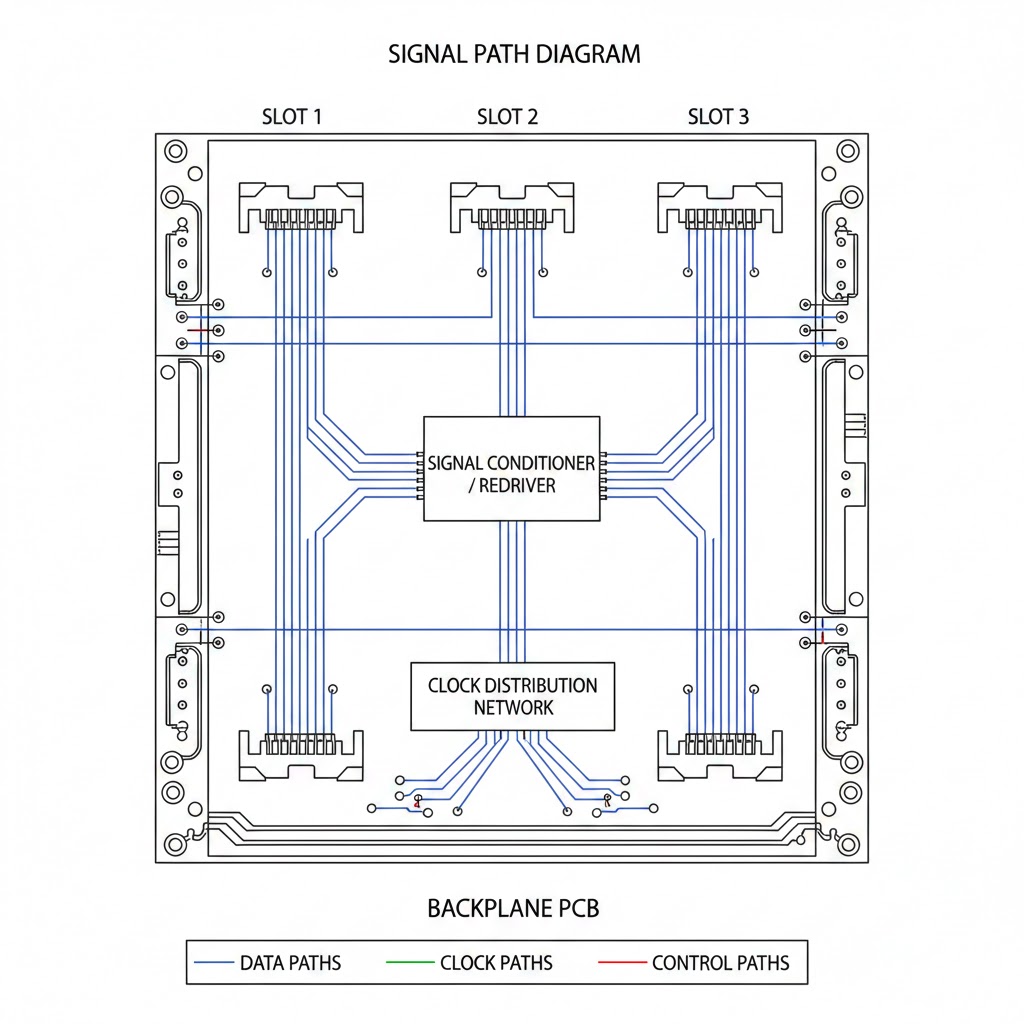
✅ Backplane Channels Explained
A backplane channel is the complete electrical path that includes:
PCB transmission lines
Vias and back-drilling
High-speed board-to-board connectors
Plug-in module pads/launch geometries
These channels support high-speed SERDES signals such as 10G, 25G, 50G, and 100G Ethernet lanes.
Backplane channels face unique challenges:
High insertion loss
Crosstalk between parallel traces
Impedance discontinuities
Connector parasitics
Short-distance but high-attenuation environments
Therefore, standards and design practices must be strictly adhered to.
✅ Backplane Standards (PICMG, VITA, IEEE)
Backplane systems often adhere to industry standards to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
1. PICMG Backplanes
Used in industrial PCs and embedded systems, such as:
PICMG 1.3 for PCI Express
Compact PCI systems
2. VITA / VPX / OpenVPX
Rugged military and telecom platforms use VPX backplanes with high-density connectors and defined fabric topologies.
3. IEEE Backplane Ethernet Standards
Backplane Ethernet is defined under the IEEE 802.3 standards:
10GBASE-KR — 10G Ethernet over backplane
40GBASE-KR4 — 4×10G lanes
100GBASE-KP4 — PAM4 modulation with FEC
IEEE 802.3bj — defines electrical parameters for 100G backplane/copper channels
These standards define channel insertion loss, equalization, and link-training procedures.
✅ Backplane Architecture Types
▷ Passive Backplanes
Contain mainly connectors and traces.
Advantages: low cost, high reliability, long lifecycle.
▷ Active Backplanes
Contain switches, retimers, clocking ICs, or signal-conditioning devices.
▷ Midplanes
A backplane located in the center of the chassis, allowing front-and-rear module connections (common in blade servers).
✅ High-Speed Backplane Design Challenges
Signal Integrity (SI) Factors
Crosstalk (NEXT & FEXT)
Channel skew & jitter margin
Backplane designers must optimize stack-up, dielectric materials, copper roughness, via design, connector footprint, and routing strategy.
High-Speed LAN Magnetics for Backplane Systems
High-speed systems also require reliable I/O modules.
LINK-PP provides a wide portfolio of RJ45 connectors with integrated magnetics (ICMs) used in backplane-based platforms (switches, servers, telecom equipment).

Suitable for:
Backplane-attached networking modules
Switch management boards
Fabric-control cards
Embedded industrial platforms
These connectors meet IEEE 802.3 electrical requirements and provide excellent EMI and SI performance.
✅ Backplane Use Cases
● Data Center & Enterprise Networking
Switches and routers use backplanes to interconnect line cards at 40G/100G speeds.
● Telecom (5G, OLT/BBU)
High-density chassis rely on backplanes to carry aggregated throughput between control, power, and signal units.
● Industrial and Military Systems
Rugged VPX backplanes support mission-critical, shock- and vibration-resistant operation.
● Storage Systems
SAS/SATA/NVMe backplanes provide hot-swap drive connectivity and enclosure management.
✅ Backplane vs Midplane vs Cable Assemblies
Backplane
Internal PCB
Short-reach, high-bandwidth
Multi-slot design
Midplane
Separates front and rear modules
Reduces mechanical complexity
Used in blade servers
Cable Assemblies (DAC/AOC)
Flexible
External cabling
Lower density but longer distances
✅ Conclusion
Backplanes are the backbone of high-performance systems, enabling reliable, high-speed, and scalable internal connectivity for modern Ethernet, telecom, industrial, and embedded platforms.
By combining robust backplane architecture with high-quality components—such as LINK-PP RJ45 ICMs —system designers can achieve excellent signal integrity, reduced EMI, and long-term reliability in demanding applications.
✅ Also See (Related Technical Resources)
To explore more high-value networking and hardware concepts, check out these related LINK-PP technical resources:




