PROFIBUS (Process Field Bus) is one of the world’s most established fieldbus standards, widely used in industrial automation to connect controllers, sensors, actuators, and distributed I/O modules. Standardized under IEC 61158, it offers deterministic serial communication, long-distance coverage, and robust real-time performance. While Ethernet-based technologies such as PROFINET are increasingly adopted, PROFIBUS remains essential in many factories due to its maturity, reliability, and vast installed base.
This guide explains PROFIBUS terminology, protocol types, network architecture, and practical applications. It also highlights how LINK-PP industrial-grade RJ45 connectors support hybrid PROFIBUS–Ethernet systems in modern automation.
✅ What Is PROFIBUS?
PROFIBUS is an open, vendor-neutral fieldbus protocol designed for industrial communication between PLCs, field devices, and control systems. Unlike Ethernet, it uses serial communication—mainly over RS-485 or MBP—to provide deterministic and stable cyclic data exchange.
Key Characteristics
Deterministic real-time field communication
Cable distances up to 1,200 meters per RS-485 segment
Multi-drop bus topology for simple installation
Wide ecosystem of certified devices
Strong reliability in electromagnetic and harsh environments
✅ PROFIBUS Protocol Types
▶ PROFIBUS DP (Decentralized Peripherals)
PROFIBUS DP is the most commonly deployed version, optimized for factory automation and high-speed device communication.
1. Technical Features
Baud rates up to 12 Mbps
RS-485 physical layer
Cyclic and acyclic data exchange
Supports remote I/O, sensors, actuators, and drives
2. Typical Applications
Assembly lines
Material handling
CNC and robotics systems
High-speed machine control
▶ PROFIBUS PA (Process Automation)
Designed for hazardous and process-oriented environments, PROFIBUS PA is widely used in chemical, energy, and pharmaceutical industries.
1. Technical Features
Based on MBP (Manchester Bus Powered)
31.25 kbps baud rate
Power and data on the same pair of wires
Intrinsically safe variants for explosive environments
2. Typical Applications
Flow, pressure, and temperature instruments
Field measurement devices
Distributed control systems in process plants
✅ How PROFIBUS Communication Works
Master/Slave Architecture
PROFIBUS operates with master devices (PLCs, DCS controllers) managing communication cycles, while slave devices (sensors, actuators, I/O modules) respond within predefined time slots.
Deterministic Cyclic Data Exchange
The controller polls all devices cyclically, ensuring predictable timing critical for automation processes.
Token Passing
In multi-master networks, a token-passing mechanism ensures orderly network control between masters.
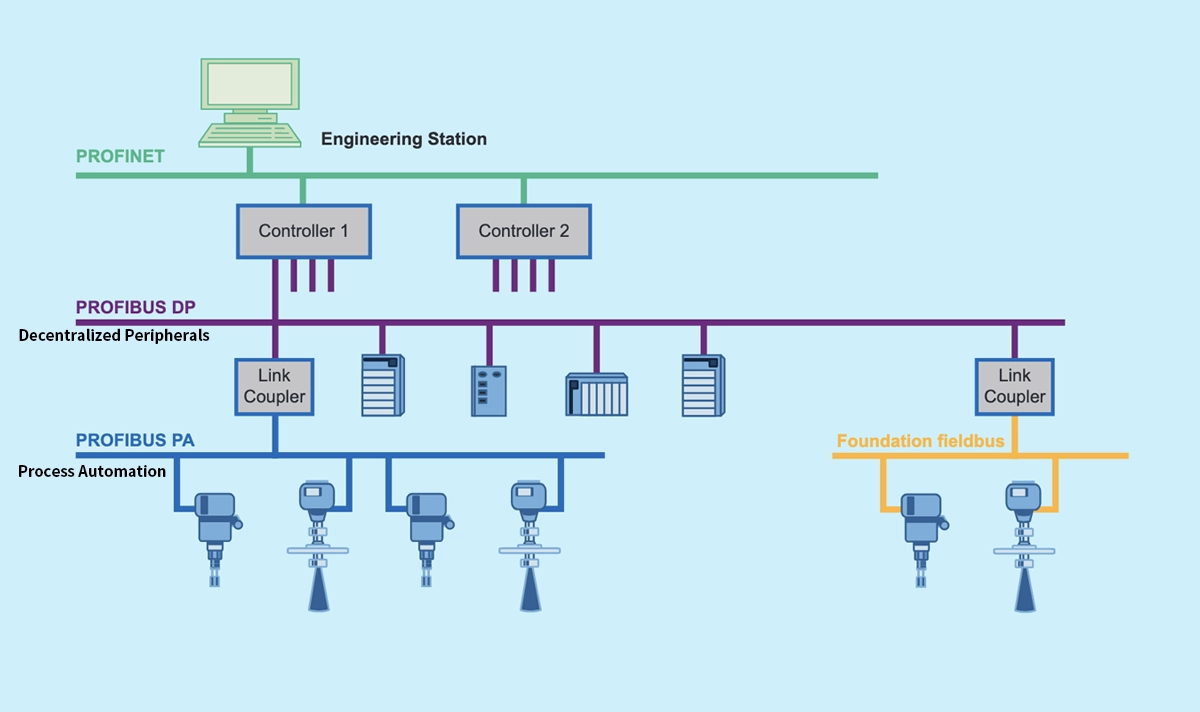
✅ Network Structure and Physical Layer
PROFIBUS DP Using RS-485
Linear bus topology
32 devices per segment directly (more with repeaters)
Shielded twisted-pair cable
Termination is required at both ends
PROFIBUS PA Using MBP
Two-wire system carrying both data and power
Long-distance capability
Supports intrinsically safe field devices
✅ Advantages of PROFIBUS
♦ Proven Reliability
Its robust physical layer makes PROFIBUS highly resistant to noise, interference, and harsh plant conditions.
♦ Cost Efficiency
Affordable device pricing and simple installation make PROFIBUS a cost-effective fieldbus option.
♦ Mature, Stable Technology
With decades of global adoption, it offers excellent long-term support and diagnostic tools.
♦ Easy Integration With Legacy Equipment
Ideal for plants requiring modern control upgrades without a complete network replacement.
✅ PROFIBUS vs. PROFINET
Feature | PROFIBUS | |
|---|---|---|
Technology | Serial RS-485/MBP | Industrial Ethernet |
Speed | Up to 12 Mbps | Up to Gigabit Ethernet |
Distance | Very long | Standard Ethernet limits |
Determinism | High | RT/IRT options |
Installation | Bus topology | Star/line/ring/tree |
Applications | Legacy and stable systems | Modern high-speed systems |
Many plants deploy both protocols—PROFIBUS at the field level and PROFINET or Ethernet upstream.
✅ Hardware Considerations in PROFIBUS Systems
PROFIBUS field devices typically use RS-485 or MBP connectors such as DB9, terminal blocks, or PA couplers. However, many hybrid PLCs, gateways, HMIs, and DCS modules also include Ethernet ports for management, engineering, diagnostics, or PROFINET connectivity.
When RJ45 Connectors Matter in PROFIBUS Environments
LINK-PP integrated RJ45 connectors play a key role in:
PROFIBUS–PROFINET gateways
PLCs featuring both serial and Ethernet ports
Industrial switches used in mixed-architecture networks
SCADA and engineering workstations connected via Ethernet

Benefits of LINK-PP Industrial RJ45 Connectors
Robust shielding for EMI-heavy industrial sites
Integrated magnetics for strong Ethernet PHY performance
Stable data transmission in automation panels
Compact, durable design for industrial controllers
▶ Product catalog:
LINK-PP Integrated RJ45 Connector Series
✅ Common PROFIBUS Use Cases
1. Factory Automation
Motors and drives
Conveyor systems
Packaging and handling machinery
2. Process Automation
Field sensors and transmitters
Valve positioners
Monitoring and control loops
3. Plant Modernization
PROFIBUS remains the preferred option for stable legacy systems requiring long-term reliability.
✅ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is PROFIBUS still used today?
Yes. Despite the rise of Industrial Ethernet systems, PROFIBUS remains widely used, especially in process industries and legacy manufacturing facilities. Its long-term stability and extensive installed base keep it relevant.
Q2: What is the main difference between PROFIBUS DP and PA?
DP is designed for high-speed factory automation using RS-485, while PA is optimized for process environments, uses MBP cabling, and supports intrinsically safe devices.
Q3: How far can PROFIBUS signals travel?
RS-485 PROFIBUS DP supports up to 1,200 meters at lower baud rates. PROFIBUS PA allows even longer distances depending on power and topology.
Q4: Can PROFIBUS and PROFINET operate together?
Yes. Many systems use PROFIBUS at the field level and PROFINET for backbone communication. Gateways and hybrid PLCs bridge the two protocols.
Q5: Why are RJ45 connectors relevant if PROFIBUS does not use Ethernet?
Modern controllers and gateways often combine PROFIBUS ports with Ethernet interfaces for diagnostics, configuration, SCADA connectivity, or PROFINET communication. High-quality RJ45 connectors ensure stable Ethernet links in these mixed networks.
✅ Conclution
PROFIBUS is a robust and proven fieldbus protocol widely used for connecting industrial devices in both manufacturing and process automation. Its deterministic timing, long-distance capability, and strong reliability make it ideal for stable automation environments. As modern plants increasingly integrate fieldbus with Ethernet-based networks, LINK-PP’s industrial-grade RJ45 connectors provide reliable connectivity between controllers, gateways, and SCADA systems—ensuring long-term performance in demanding industrial applications.


